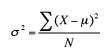- How do I calculate Variance?
- How Much Can Data Vary?
- Variance of a Binomial Distribution
- Population Variance
- Sample Variance
Variance measures how far a data set is spread out. It is mathematically defined as the average of the squared differences from the mean.
How do I calculate it?
The variance for a population is calculated by:
- Finding the mean(the average).
- Subtracting the mean from each number in the data set and then squaring the result. The results are squared to make the negatives positive. Otherwise negative numbers would cancel out the positives in the next step. It’s the distance from the mean that’s important, not positive or negative numbers.
- Averaging the squared differences.
However, it’s more usual in statistics to find the variance for a sample. When you calculate it for a sample, divide by the sample size minus one (Why use n-1?) when calculating the average squared difference in Step 3 above. See: Finding Sample Variance.
Use our online var. and standard deviation calculator, which shows you the step-by-step calculations for your individual data set. You can also calculate the σ2 in Minitab.
Need help with a homework question? Check out our tutoring page!
Standard Deviation
The square root of the variance is the standard deviation. While var. gives you a rough idea of spread, the standard deviation is more concrete, giving you exact distances from the mean.
Variance on a TI-83
Variance on a TI-83 Overview
You could find the standard deviation for a list of data using the TI 83 calculator and square the result, but you won’t get an accurate answer unless you square the entire answer, including all of the significant digits. There’s a “trick” to getting the TI-83 variance, and it involves copying the standard deviation to the Home screen and then squaring it to get the variance.
Variance on a TI-83: Steps
Example problem: Find the variance for the heights of the top 12 buildings in London, England. The heights, (in feet) are: 800, 720, 655, 655, 625, 600, 590, 529, 513, 502, 502, 502.
Step 1: Enter the above data into a list. Press the STAT button and then press ENTER. Enter the first number (800), and then press ENTER. Continue entering numbers, pressing ENTER after each entry.
Step 2: Press STAT.
Step 3: Press the right arrow button (the arrow keys are located at the top right of the keypad) to select Calc.
Step 4: Press ENTER to highlight 1-Var Stats.
Step 5: Press ENTER again to bring up a list of stats.
Step 6: Press VARS 5 to bring up a list of the available Statistics variables.
Step 7: Press 3 to select “Sx” which is our standard deviation.
Step 8: Press x2, then Enter to display the variance, which is 9326.628788.
That’s how to find the Variance on a TI-83!
Back to Top
Lost your guidebook? You can download a new one here from the Texas Instruments website.
Minitab Instructions
How to find the Variance in Minitab: Steps
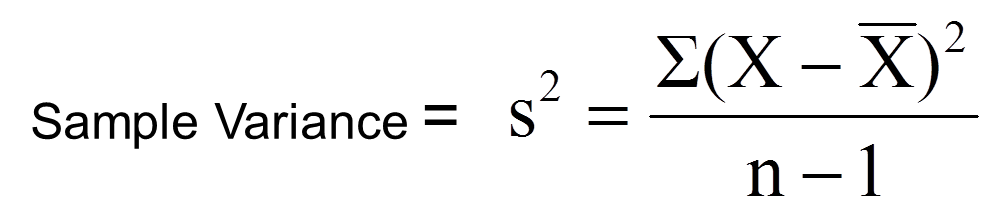
Example question: Find the variance for the following sample: 12, 13, 24, 24, 25, 26, 34, 35, 38, 45, 46, 52, 53, 78, 78, 89
Step 1: Type your data into a column in a Minitab worksheet.
Step 2: Click “Stat”, then click “Basic Statistics,” then click “Descriptive Statistics.”
Step 3: Click the variables you want to find the variance for and then click “Select” to move the variable names to the right window.
Step 4: Click “Statistics.”
Step 5: Check the “Variance” box and then click “OK” twice. The variance in Minitab will be displayed in a new window. The variance for this particular data set is 540.667.
That’s it!
How Much Can Data Vary?
The smallest a variance gets is zero, but technically, it can be infinite with numbers in the millions or even billions and beyond.
Variance of a Binomial Distribution
A binomial distribution is a simple experiment where there is “success” or “failure.” For example, choosing a winning lottery ticket could be a binomial experiment (you either win or lose!). Tossing a coin to try and get heads is also binomial (with tossing a heads being a “success” and a tails a “failure”). The formula for the variance of binomial distribution is n*p (1-p) or n*p*q. The two formulas are equivalent because q = (1-p).
Example problem: If you flip a coin 50 times and try to get heads, what is the variance of binomial distribution?
Step 1: Find “p”. The first step to solving this problem is to realize that the probability of getting a heads is 50 percent, or .5. Therefore, “p” (the probability) is .5.
Step 2: Find “q”, or 1-p. These two are equivalent. They are the probability of not getting a heads (in other words, the probability of getting a tails). 1 – 0.5 = 0.5. Therefore, “q” (or 1 – p) = 0.5.
Step 3: Multiply Step 1 (p) by Step 2 (q) by “n” (the number of trials). We are flipping the coin 50 times, so the number of trials is 50 (n = 50).
N * p * q = 50 * .5 * .5 = 12.5.
The var. of binomial distribution for flipping a coin 50 times is 12.5.
OK, So what does the Binomial Variance mean?
In essence, not a lot! The variance isn’t used for much at all, except for calculating standard deviation. For example, the standard deviation for this particular binomial distribution is:
√12.5 = 3.54.
You’ll use the variance for things like calculating z-scores (this typically comes later in a stats class, after normal distributions), which has a standard deviation in the bottom of the formula:
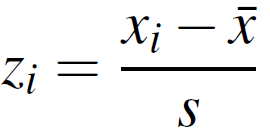
Back to Top
Population Variance
The population variance is a type of parameter. If you aren’t sure what a parameter is, you may want to review:
What is the Difference Between a Statistic and a Parameter?
How to find the Population Variance.
Most of the time in statistics, you’ll want to find the sample variance, not the population variance. Why? Because statistics is usually all about making inferences from samples, not populations. If you had all of the data from a population, there would be no need for statistics at all! That said, there really is very little difference between the formula for the population variance and the formula for the sample variance. If you have sample data, you can still use this formula. You’d just need to insert your data into the columns instead of your population data. If you prefer to plug the numbers straight into the formula, just make sure you use the population mean and not the sample mean(![]() ). In addition, the most common sample variance formula uses n-1 in the denominator instead of n.
). In addition, the most common sample variance formula uses n-1 in the denominator instead of n.
Example problem: Find the population variance for the following set of numbers: 28, 29, 30, 31, 32.
Step 1: Draw a table. Label the columns as shown and then write down your X values (the items in your population) in column 1:
| X | X-μ | (X-μ)^2 |
| 28 | ||
| 29 | ||
| 30 | ||
| 31 | ||
| 32 |
Step 2: Find the mean. The mean for this set of data is (28 + 29 + 30 + 31 + 32) / 5 = 30.
Step 3: Fill in column 2. This column is your X value minus the mean. For example, the first entry is 28 – 30 = -2.
| X | X-μ | (X-μ)^2 |
| 28 | -2 | |
| 29 | -1 | |
| 30 | 0 | |
| 31 | 1 | |
| 32 | 2 |
Step 4: Square the values from Step 3 and place those squares in the third column:
| X | X-μ | (X-μ)^2 |
| 28 | -2 | 4 |
| 29 | -1 | 1 |
| 30 | 0 | 0 |
| 31 | 1 | 1 |
| 32 | 2 | 4 |
Step 5: Add up all of the numbers in column 3 (this is the summation Σ part of the formula):
4 + 1 + 0 + 1 + 4 = 10
Step 6: Divide by the number of items in your data set:
10 / 5 = 2
The population variance for this set of data is 2.
Check out our YouTube channel for hundreds of step-by-step statistics videos.
References
Kenney, J. F. and Keeping, E. S. Mathematics of Statistics, Pt. 2, 2nd ed. Princeton, NJ: Van Nostrand, 1951.
Papoulis, A. Probability, Random Variables, and Stochastic Processes, 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, pp. 144-145, 1984.