The jackknife (“leave one out”) can be used to reduce bias and estimate standard errors. It is an alternative to the bootstrap method.
Comparison to Bootstrap
Like the bootstrap, the Jackknife involves resampling. The main differences are:
- The bootstrap involves sampling with replacement, while the jackknife involves sampling without replacement.
- The bootstrap tends to be more computationally intensive.
- The jackknife’s estimated standard error tends to be larger than bootstrap resampling.
Overview of the Jackknife Procedure
The basic idea is to calculate the estimator (e.g. the sample mean) by sequentially deleting a single observation from the sample. The estimator is recomputed until there are n estimates for a sample size of n. As a simple example, let’s say you had five data points X1, X2, X3, X4, X5. You would calculate the estimator five times, for:
- X1, X2, X3, X4, X5.
- X2, X3, X4, X5.
- X3, X4, X5.
- X4, X5.
- X5.
Once you have your n estimates
![]() ,
,
the standard error is calculated with the following formula:
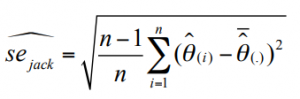
Why Use Jackknife Estimation?
Jackknife estimation is usually used when it’s difficult or impossible to get estimators using another method. For example:
- No theoretical basis is available for estimation,
- The statistics’s function is challenging to work with (e.g. a function with no closed form integral, which would make the usual method (the delta method) impossible),
For large samples, the Jackknife method is roughly equivalent to the delta method.
References
The Bootstrap and Jack knife. Retrieved November 2, 2019 from: https://www.biostat.washington.edu/sites/default/files/modules/2017_sisg_1_9_v3.pdf
McIntosh, A. The Jack knife Estimation Method. Retrieved November 2, 2019 from: http://people.bu.edu/aimcinto/jackknife.pdf
Ramachandran, K. & Tsokos, C. (2014). Mathematical Statistics with Applications in R. Elsevier.