What is the Exponential-Logarithmic Distribution?
The exponential-logarithmic (EL) distribution is a log-series mixture distribution of exponential random variables, introduced by Tahmasbi and Rezaei in 2008 [1]. It is created when the rate parameter for the exponential distribution is randomized by the logarithmic distribution.
The distribution is used to model decreasing failure or survival rates; In other words, it can be used to model processes that improve over time. An example would be a trainee machine operator that makes fewer errors as training progresses. In reliability analysis, the distribution is based on the concept of modeling reliability when time-to-failure happens when an unknown number of initial “defects” on a components is considered [2]. It is defined on the interval [0, ∞).
One way to define the distribution is by the function [3]
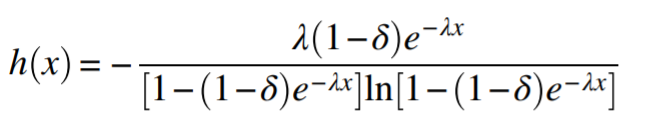
Sometimes you’ll see “p” instead of δ and β instead of λ.
PDF & CDF of the Exponential-Logarithmic Distribution
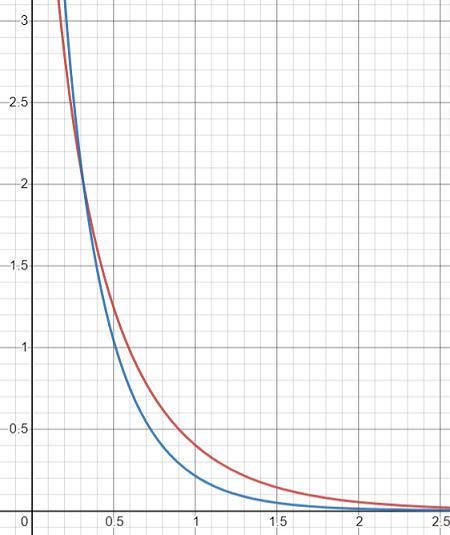
The probability density function (PDF) of the exponential-logarithm distribution is:
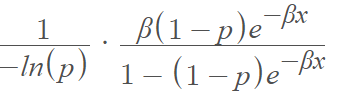
The cumulative distribution function is:
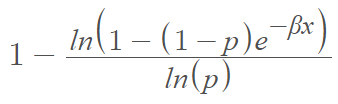
References
Graph created with Desmos.
[1] Tahmasbi, R. and Rezaei, S. (2008). A two-parameter lifetime distribution with decreasing failure rate. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis 52(8):3889-3901
[2] Rahmouni, M. & Orabi, A. (2018). A Generalization of the Exponential-Logarithmic Distribution for Reliability and Life Data Analysis. Retrieved January 2, 2022 from:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1803.01156.pdf
[3] King, M. Statistics for Process Control Engineers: A Practical Approach. (2017). Wiley.