A Trifolium curve (or 3-petalled rose curve) is a special case of the folium curve (where b = a), with three smooth parts that intersect each other transversally [1]. The word folium means “leaf-shaped” [2].
The Cartesian equation is:
(x2 + y2)(y2 + x(x + a)) = 4axy2.
Alternatively,
(x2 + y2)2 = a(x3 – 3xy2).
The variable a affects the size of the trifolium, not its shape. The shape of the trifolium is determined by the ratio between the upper and lower wheels that construct the curve (shown in the above image).
Two other special cases of the folium are the simple folium, and the double folium. They correspond to b = 4a, b = 0.
The curve was first studied in 1609 by Kepler, which gives it it’s alternate name, Kepler’s Folium. It is also called paquerette de mélibée [3] where “paquerette” is French for “wild daisy.” The curve was also studied by Longchamps in 1885, and Brocard and d’Ocagne in 1887 [4].
Trifolium Curve: Alternate Definitions
Dana-Picard and Kovacs [5] define a regular trifolium (or trefoil) as a plane curve with the implicit equation
(x2 + y2)2 = ax(x2 – 3y2),
where a is a positive real parameter.
The curve can also be defined by the polar equation r(t) = a | cos(3 θ) |.
The polar equation r = -a cos (3 θ) describes a trifolium with a lobe along the negative axis.
Lawrence [6] defines a trifolium as a folium curve with b ∈ (0, 4a), but this definition is not commonly used [7].
Area of a Trifolium Curve
The area of a trifolium curve is given by the integral
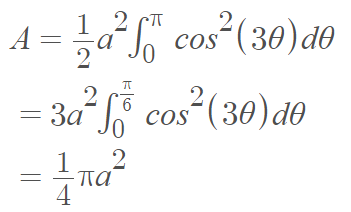
Folium Curve
folium of Descartes (x3 + y3 = 3xy) which is a single “leaf” with one node and two asymptotes at the ends.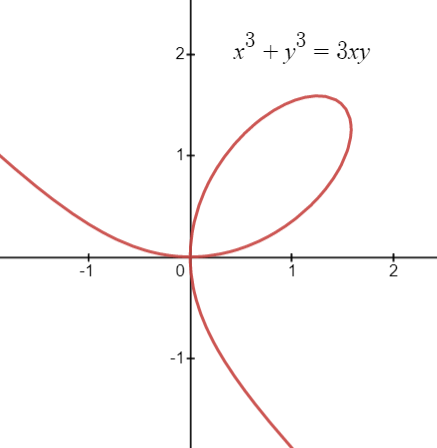
References
Folium created with Desmos.com
[1] Dragovic, V. & Radnovic, M. (2011). Poncelet Porisms and Beyond: Integrable Billiards, Hyperelliptic Jacobians and Pencils of Quadrics. Springer Basel.
[2] MacTutor. Curves : Trofolium. Retrieved February 2, 2022 from: https://mathshistory.st-andrews.ac.uk/Curves/Trifolium/
[3] Apéry, F. Models of the Real Projective Plane. Braunschweig, Germany: Vieweg, p. 85, 1987.
[4] Tan, S. (2020). Handbook of Famous Plane Curves Using Mathematica. Lulu.com.
[5] Dana-Picard, T. & Kovacs, Z. (2021). Offsets of a regular trifolium. Retrieved February 22, 2022 from: https://www.academia.edu/64611330/Offsets_of_a_regular_trifolium
[6] Lawrence, J. D. A Catalog of Special Plane Curves. New York: Dover, pp. 152-153, 1972.
[7] Giedre, S. Mathematics Curves. Retrieved February 22, 2022 from: https://www.academia.edu/23149113/Mathematics_Curves