Statistics Definitions > L-Estimator
What is an L-Estimator?
An L-estimator is a linear combination of statistics based on order statistics, or sample quantiles. L-estimators were first outlined by Daniel (1920) and were revived in robustness studies thirty years later. They have the advantage of being robust and simple to use, but tend to have problems with low efficiency.
Not all L-estimators are robust (for example, the minimum, maximum and mean are not considered robust) and some have better efficiency than others. L-statistics with multiple (correct) weights will tend to be more efficient than those with fewer weights or poorly chosen weights.
L-estimators, Tn for a sample size n, are defined by:
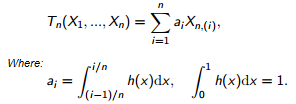
Where:
- Xn are the order statistics,
- ai are weight factors.
L-Estimator Examples
- Jurečková and Picek (2006) suggest the midrange as a simple example of an L-estimator, which is defined as:
Tn = (X1:n + Xn:n) / 2 - The range is a simple L-estimator of distribution scale: Rn = largest value – smallest value = Xn:n – X1:n.
- The median is one of the more well known order statistics that is also an L-estimator.
- The α trimmed mean, which discards the smallest and largest data points, includes the mean (α = 0), the median (α = 0.5).
- Winsorized mean.
- Tukey’s trimean.
A special class of L-estimators, called kernel quantile estimators, use a kernel (a density function) as its weight function. Many other L-estimators have been proposed by multiple authors including Harrell and Davis (1982), who proposed a new distribution-free (non parametric) estimator, and Kaigh (1983) who proposed a type of non-parametric U statistic as a quantile estimator.
References:
Daniel, C. (1920). Observations weighted according to order. Amer. J. Math. 42, 222–236.
Harrell, F.E. and Davis, C.E. (1982), “A New Distribution-Free Quantile Estimator,” Biometrika, 69, 635-640
Jurečková,J & Picek, J. (2006). Robust statistical methods with R: Boca Raton, Fla. Chapman and Hall/CRC. ISBN 1-58488-454-1, 197 p.
Kaigh, W.D. (1983), “Quantile Interval Estimation,” Communications in Statistics, Part A – Theory and Methods, 12,2427-2443.
Sheather, S. and Marron, J. Kernel Quantile Estimators. Journal of the American Statistical Association
Vol. 85, No. 410 (Jun., 1990), pp. 410-416