What are Observed Variables?
Observed variables (sometimes called observable variables or measured variables) are measured by the researcher. If you’re working with structural equations models (SEM), they are data that actually exists in your data files—data that has been measured and recorded. They can be discrete variables or continuous variables.
Observed variables can also be sub-classified with other variable types. For example, an observed exogenous variable is not controlled by other variables in the system (it is roughly equivalent to an independent variable in an experiment) while an observed endogenous variable is affected by other variables in the system (it is roughly equivalent to a dependent variable in an experiment). Further classifications are also possible, such as dichotomous observed endogenous variables or dichotomous observed exogenous variables, which are binary (i.e. they have a value of 0 or 1).
Observed vs. Latent Variables
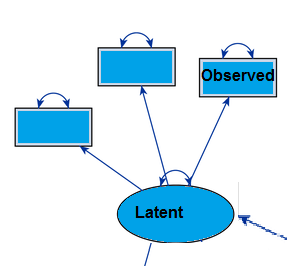
The opposite of an observed variable is a latent variable, also referred to as a factor or construct. A latent variable is hidden, and therefore can’t be observed. While observed variables are the only type of variable used in regression analysis, SEM can handle other types of variables including latent, unobserved and theoretical variables. Observed variables are represented by rectangular nodes in SEM and latent variables are represented by circles or ellipses. An important difference between the two types of variables is that an observed variable usually has a measurement error associated with it, while a latent variable does not.
Examples of Observed Variables
Let’s say you were analyzing results from a major depression inventory. Feelings of sadness, lack of interest in daily activities and lack of self-confidence are all measured by the inventory and are therefore observed variables. Other examples:
- Allen’s Affective Commitment Scale,
- Gender,
- Grade Point Averages,
- IQ Test scores,
- Minnesota Job Satisfaction Scale,
Related Variables
- Manifest variable: an observed variable that indicates the presence of a latent variable.