Statistics Definitions > Stanine Score
What is a Stanine Score?
A stanine (“standard nine”) score is a way to scale scores on a nine-point scale. It can be used to convert any test score to a single-digit score. Like z-scores and t-scores, stanines are a way to assign a number to a member of a group, relative to all members in that group. However, while z-scores and t-scores can be expressed with decimals like 1.2 or 3.25, stanines are always positive whole numbers from 0 to 9.
Stanines are also similar to normal distributions. You can think of these scores as a bell curve that has been sliced up into 9 pieces. These pieces are numbered 1 through 9, starting at the left hand section. However, where a standard normal distribution has a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1, stanines have a mean of 5 and a standard deviation of 2.
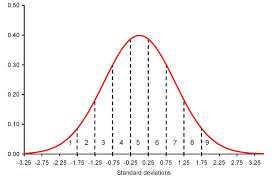
What do Stanines mean?
A person with a score of 9 is in the top 4% of the scorers, while a person with a score of 1 is in the bottom 4%. These types of scores allow you to easily tell if a score is below the mean (a score of 5) or above the mean.
How to Convert a Score to a Stanine
Step 1: Rank the scores from lowest to highest.
Step 2: Assign a stanine score to your scores from Step 1:
| Stanine score | Percentage of scores |
| 1 | Bottom 4% |
| 2 | Next bottom 7% |
| 3 | Next bottom 12% |
| 4 | Next Bottom 17% |
| 5 | Middle 20% |
| 6 | Next top 17% |
| 7 | Next top 12% |
| 8 | Next top 7% |
| 9 | Top 4% |
The mean lies in the middle of the fifth score, cutting the center 20% into two parts.
Loss of Information
These scores are a very simple way of categorizing items into top, middle and bottom percentages. This simplicity means that it’s a very imprecise way to measure anything. Everyone in the same stanine receives the same score. For example, a person at the bottom of the 5th is almost 20 percentage points below the person at the top of the 5th. These differences are what is called “loss of information.”