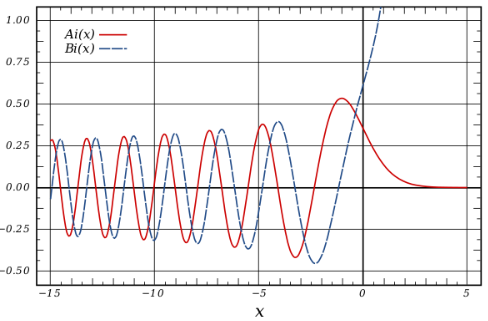
Airy functions are particular solutions of the Airy equation (also called the Stokes equation).
They were first developed by astronomer Sir George Biddell Airy (1801-1892), during his investigations into optic diffractions. They have a wide variety of applications and are used in fields as diverse as quantum mechanics, electromagnetics and combinatorics. A different function developed by Airy is important in astronomy and microscopy.
Definitions for the Airy Function
Several definitions exist. The most common is graphed above and is the solution to the Airy differential equation
φ′′ ± k2 φ x = 0.
Other definitions include using special functions (like Bessel functions) to define the Airy function, or as an integral (Milton, n.d.):
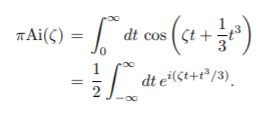
Or as a power series:
![]()
Despite the different look of the function with the different representations, they are all equivalent.
The Airy Disk Function
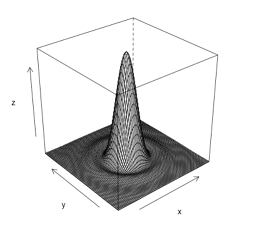
Notation
The usual notation for Airy functions is Ai and Ab, although there is other notation. For example, Scientific Notebook (SNB) uses “AiryAi” and “AiryBi.
References
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, C. A. (Eds.). Airy Functions. §10.4 in Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, 9th printing. New York: Dover, pp. 446-452, 1972.
Banderier, C. & Louchard, G. Philippe Flajolet and the Airy Function. Retrieved December 4, 2019 from: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.696.2138&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Fermilab. Airy Disk. Retrieved December 5, 2019 from: https://cdcvs.fnal.gov/redmine/projects/jdemsoc-private/wiki/Diffraction_from_a_circular_aperature
Gallant, J. (2012). Doing Physics with Scientific Notebook: A Problem Solving Approach. John Wiley & Sons.
Hazewinkel, M. (1994). Encyclopaedia of Mathematics (set). Springer Science & Business Media.
Milton, K. Chapter 9: Asymptotic Expansions. Retrieved December 4, 2019 from: http://www.nhn.ou.edu/~milton/p5013/chap9.pdf
Calculus II, Section 11.8, #36 Power Series.