Statistics Definitions > Ratios and Rates
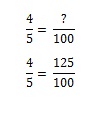
Ratio Definition
A ratio is a comparison of two numbers. It can be written in many ways. For example, the ratio of 5 to 9 can be expressed as:
- 5 to 9
- 5 out of 9
- 5:9
- 5/9
Rate Definition
A rate is a specific type of ratio that usually tells you how long it takes to do something. For example, a rate might be 100 miles / 10 hours. In simple English, that’s saying it takes 10 hours to travel 100 miles. We can reduce that fraction to a “per hour” statement (by using the greatest common factor or another similar method); simplifying, it becomes 10 miles per hour.
In most cases, a rate will have time in the denominator and is a measure of how long it takes to do something; the numerator will also have different units from the denominator, as in the above example. However, there are exceptions in common usage (like “tax rates” and “interest rates”), which have the same units and measure “something else” like interest charged per amount loaned.
Ratios and Rates: Related Terms
References
Doctor Peterson. Rate vs. Ratio. Article posted on The Math Forum. Retrieved June 2, 2018.